

Too much pineapple? Here’s what happens to your body:
Whether it’s served fresh on a fruit platter, grilled with savory dishes, blended into a smoothie, or (controversially) added to pizza, pineapple is undeniably one of the most popular tropical fruits in the world. With its bold, tangy-sweet flavor and eye-catching appearance, it brings a tropical flair to any meal.
But while pineapple offers a host of health benefits, eating too much of it can cause some unwanted side effects. Here’s what you should know about overindulging in this juicy fruit.
The Nutritional Power of Pineapple:
Pineapple isn’t just a delicious tropical fruit it’s also a nutritional powerhouse that supports overall health. A single cup of fresh pineapple delivers over 100% of the recommended daily intake of vitamin C, which is essential for immune function, collagen production, and cellular protection against free radicals.
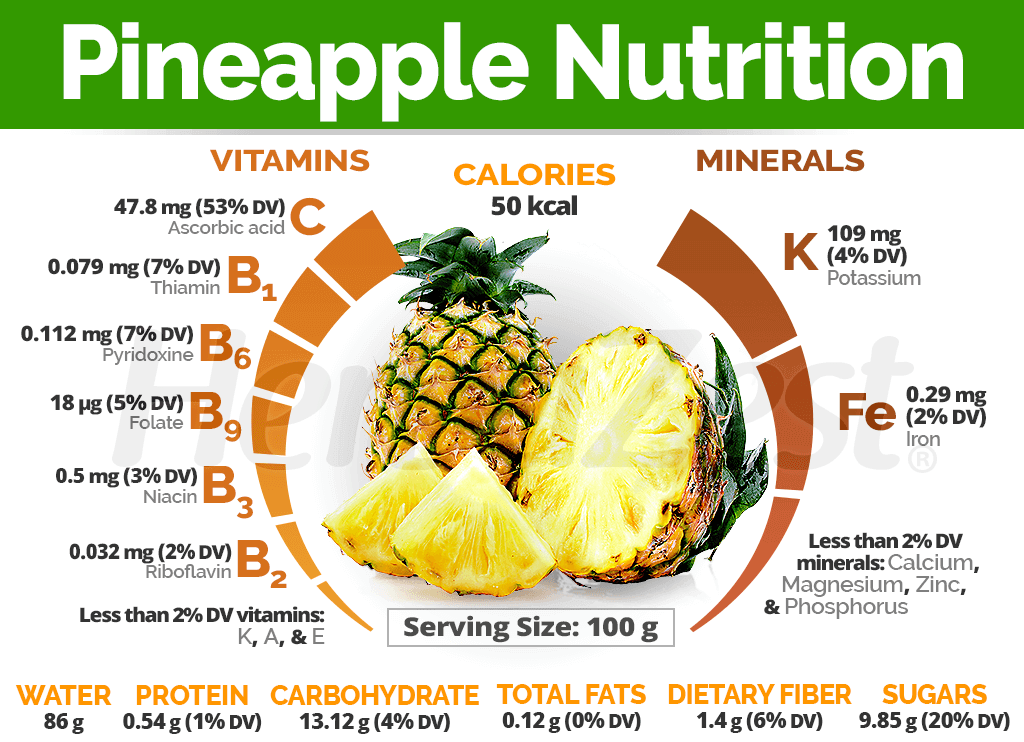
Health benefits chart:
Pineapple is also one of the best dietary sources of manganese, providing about 75% of your daily needs in just one cup. This vital mineral aids in bone formation and energy production. Additionally, pineapple contains dietary fiber, which promotes healthy digestion, stabilizes blood sugar, supports a balanced gut microbiome, and helps you feel full longer.
Another key component is bromelain, a natural enzyme with anti-inflammatory and digestive properties that assists in breaking down proteins and may help reduce swelling and promote recovery after physical exertion or surgery. Finally, pineapple is a good source of vitamin B6, which supports brain health, mood balance, and energy metabolism, making this fruit a valuable addition to a balanced diet.
Can You Eat Pineapple Every Day?
Pineapple is nutritious, but moderation is key. Here are some problems that can arise from eating too much:
Digestive Discomfort:
The fruit’s bromelain and fiber content aid digestion, but in excess, they can cause bloating, gas, or stomach cramps. Overconsumption may also lead to a tingling or burning sensation in the mouth, tongue, or lips. This is due to bromelain breaking down proteins in the mucous membranes.
Tooth Sensitivity and Decay:
Pineapple’s natural acids and sugars can wear down tooth enamel, especially when eaten frequently without good oral hygiene.
Blood Sugar Spikes:
Despite its natural sugars being healthier than added sugars, large quantities can still affect blood glucose levels. People with diabetes should be cautious and pair pineapple with protein or healthy fats to mitigate sugar spikes.
Medication Interactions:
Bromelain can interact with certain medications such as blood thinners and antibiotics. If you’re taking prescription medications, it’s best to check with your healthcare provider before regularly consuming large amounts of pineapple.
Worsening of Certain Health Conditions:
Individuals with acid reflux, IBS, or sensitivities to acidic foods may experience worsened symptoms after eating pineapple due to its high acidity.
Bottom Line:
Pineapple is a vibrant, flavorful fruit that delivers a wide range of nutrients. When eaten in moderation, it can support your health, satisfy sweet cravings, and add zest to your meals. But like any good thing, too much pineapple can lead to problems—especially for people with digestive sensitivities, diabetes, or certain medical conditions.






